Industrial automation
Industrial Automation: Transforming Manufacturing with Technology
Industrial automation, the use of control systems like computers and robots to handle different industrial processes and machinery, is revolutionizing how industries operate and produce goods. From automotive and aerospace manufacturing to food processing and electronics assembly, industrial automation enables faster, safer, and more efficient operations by minimizing human intervention. This transformation is powered by a combination of technologies, including robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and advanced sensors, all working together to optimize production and ensure consistency and quality in every output.
The Core of Industrial Automation: Efficiency and Precision
One of the central goals of industrial automation is to improve efficiency by streamlining processes, reducing production time, and minimizing errors. Automated systems operate with a high level of precision, allowing manufacturers to produce consistent, high-quality products without the risk of human error. This is especially beneficial in industries that require stringent quality standards, such as pharmaceuticals and electronics. Automation enables machines to perform repetitive tasks with speed and accuracy, enhancing overall productivity and ensuring that each product meets the desired specifications.
Enhanced Safety and Reduced Labor Demands
Industrial automation plays a crucial role in improving workplace safety by reducing the need for humans to engage in potentially dangerous tasks. Robots and automated systems can handle hazardous environments, such as extreme temperatures or exposure to toxic substances, which minimizes the risk of workplace injuries. For tasks that are physically demanding or require repetitive motion, automation helps to reduce strain on workers, ultimately enhancing their well-being and allowing them to focus on tasks that require human oversight and creativity.
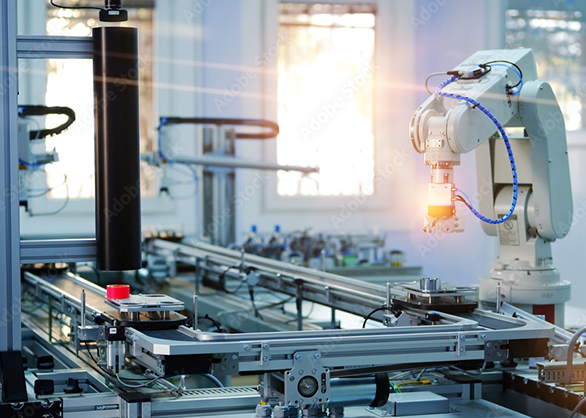
The Role of Robotics in Industrial Automation
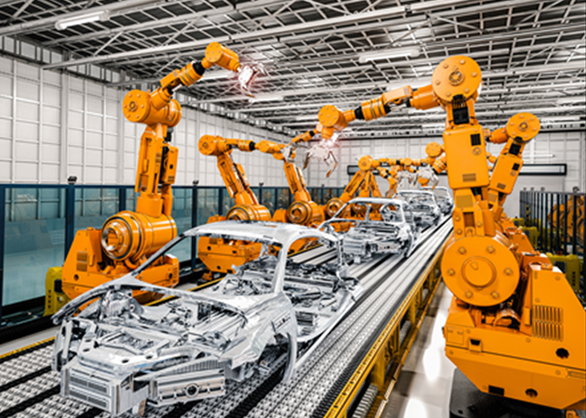
Robots are a cornerstone of industrial automation, performing tasks such as welding, assembly, painting, and packaging with high efficiency and accuracy. Advanced robotics, including collaborative robots (cobots), are designed to work alongside human operators, assisting them in complex tasks and improving overall productivity. These robots can be programmed to handle a range of operations, making them versatile assets in the manufacturing environment. The adaptability and precision of robotics mean that manufacturers can handle various tasks with a single automated system, reducing the need for specialized equipment.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Driving Smarter Automation
AI and machine learning are vital components of modern industrial automation, enabling systems to learn from data, optimize processes, and even predict potential issues before they occur. By analyzing vast amounts of data generated during production, AI algorithms can identify patterns, improve decision-making, and fine-tune processes in real-time. Machine learning also allows automation systems to adapt to changes in production requirements, making them more flexible and responsive to market demands. Predictive maintenance is one of the key applications of AI in automation, as it uses data analysis to foresee equipment failures and schedule repairs before they disrupt operations.
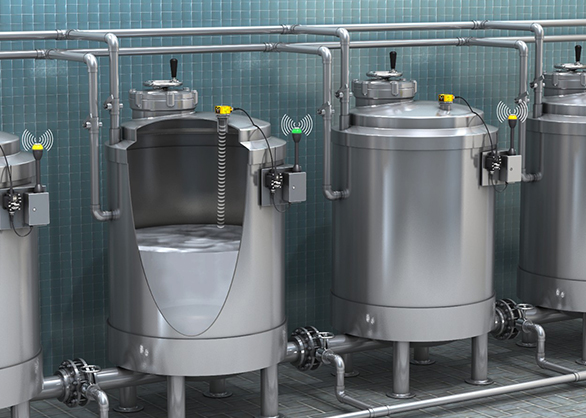
Sensors and the Internet of Things (IoT): Real-Time Monitoring and Data Collection
The integration of sensors and IoT devices in industrial automation has brought about a new level of connectivity, enabling real-time monitoring and data collection across all stages of production. Sensors track parameters such as temperature, pressure, and vibration, providing valuable insights into machine performance and product quality. With IoT, this data is transmitted to a central system where it can be analyzed to optimize production processes and enhance decision-making. Real-time monitoring also allows manufacturers to identify and resolve issues instantly, minimizing downtime and improving overall productivity.
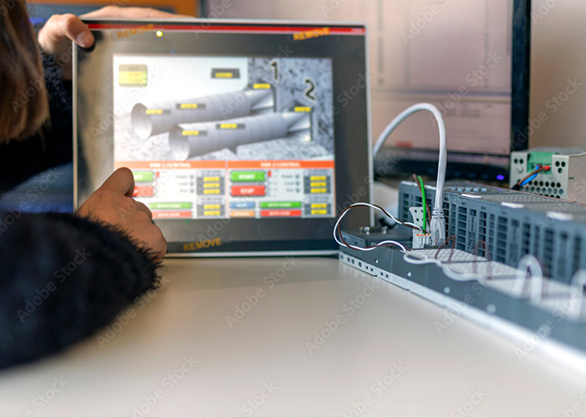
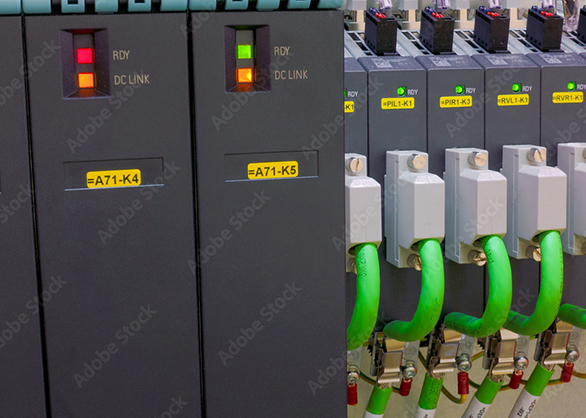
Industrial Control Systems: Coordinating Complex Processes
Industrial automation relies on sophisticated control systems, including Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and Distributed Control Systems (DCS), to manage and coordinate various operations. These systems are designed to control multiple processes simultaneously, ensuring that each step in the production line operates smoothly. PLCs and DCS systems can be programmed to execute specific tasks in a set sequence, while also allowing for adjustments based on real-time data. By controlling machinery with precision, industrial control systems reduce waste, optimize resource usage, and ensure that production runs seamlessly.
Cost Savings and Competitive Advantage
While the initial investment in industrial automation technology can be substantial, the long-term savings make it a valuable asset for manufacturers. Automated systems reduce labor costs, minimize waste, and improve energy efficiency, all of which contribute to lower operational costs over time. Furthermore, companies that adopt automation gain a competitive advantage by being able to produce high-quality goods faster and more efficiently than their competitors. This advantage becomes especially important in industries with tight profit margins, as automation helps reduce production costs and increase profitability.
Environmental Impact: Reducing Waste and Energy Consumption
Industrial automation also offers environmental benefits by reducing waste and energy consumption. Automated systems are optimized to use only the necessary amount of resources, helping to minimize waste and reduce emissions. For example, automated production lines can be programmed to recycle materials, conserve energy, and operate more sustainably. As manufacturers face increasing pressure to adopt eco-friendly practices, industrial automation provides an effective solution for achieving sustainability goals while maintaining high productivity levels.
Future Trends: Expanding the Scope of Industrial Automation
The future of industrial automation holds exciting possibilities, with advancements in AI, robotics, and IoT expected to drive even greater efficiency and innovation. Emerging technologies, such as autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) and digital twins, allow for more flexibility in manufacturing environments and offer real-time simulations to optimize production lines before implementing changes. As automation becomes more accessible, industries that have traditionally relied on manual labor, such as agriculture and construction, are beginning to adopt automated solutions. This expansion into new sectors is set to further transform the global economy, as automation enables faster, more precise, and cost-effective production.
Conclusion
Industrial automation has become an essential component of modern manufacturing, providing companies with the tools to enhance productivity, improve quality, and reduce operational costs. By harnessing the power of robotics, AI, IoT, and advanced control systems, industrial automation transforms manufacturing processes, making them more efficient, safer, and sustainable. As technology continues to evolve, industrial automation will remain at the forefront of innovation, driving progress and reshaping industries worldwide.
Here are some key features of industrial automation that have transformed modern manufacturing:
1. High Precision and Accuracy
Automated systems ensure that tasks are completed with consistent precision, minimizing the risk of human error and ensuring product quality. This is particularly critical in sectors such as electronics, pharmaceuticals, and automotive, where small inaccuracies can lead to significant defects.
2. Enhanced Productivity and Speed
Automation boosts productivity by allowing machines to perform repetitive tasks faster than human workers. These systems can run continuously without fatigue, which significantly increases production rates and enables manufacturers to meet high demand efficiently.
3. Real-Time Monitoring and Control
Through sensors and IoT integration, industrial automation systems provide real-time data about machine performance, product quality, and environmental conditions. This enables operators to monitor and control processes remotely and make quick adjustments if issues arise.
4. Predictive Maintenance
Using data from sensors and AI algorithms, predictive maintenance identifies potential machine failures before they occur, allowing companies to schedule repairs proactively. This reduces unexpected downtime, minimizes maintenance costs, and extends equipment lifespan.
5. Adaptability and Flexibility
Modern automated systems can be reprogrammed to handle various tasks, making them versatile assets in manufacturing. This flexibility allows manufacturers to quickly adapt to changes in production requirements, such as product modifications or increased demand.
6. Improved Safety
Automation helps reduce workplace hazards by performing dangerous tasks that could put human workers at risk. Robots and automated machinery can operate in extreme environments (e.g., high temperatures, toxic areas), helping to create a safer workplace and minimizing the chance of accidents.
7. Data Collection and Analytics
Automation systems collect vast amounts of data on production processes, which can be analyzed to optimize efficiency, improve quality, and reduce costs. Advanced data analytics provide insights that guide process improvements and strategic decision-making.
8. Energy Efficiency
Automated systems are designed to optimize resource usage, conserving energy and reducing waste. This leads to lower utility costs and supports environmental sustainability efforts by reducing the carbon footprint of manufacturing processes.
9. Reduced Operational Costs
Automation helps decrease the reliance on manual labor, resulting in lower labor costs and increased output. Over time, the reduction in errors, energy consumption, and maintenance costs results in significant savings, enhancing overall profitability.
10. Quality Control and Consistency
Automation enables consistent quality control by ensuring that each product or component meets predefined specifications. This consistency is crucial in industries with strict quality standards, helping to maintain brand reputation and reduce product recalls.
11. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Automation can help ensure faster production cycles and consistent quality, enabling companies to meet customer expectations for both speed and reliability. This strengthens customer relationships and boosts brand loyalty.
12. Scalability
Automated systems make it easier to scale production up or down based on demand. By implementing modular and flexible automation systems, manufacturers can add or modify components to increase capacity without overhauling the entire production line.
Industrial automation is an essential tool for modern manufacturers, enabling them to achieve unprecedented efficiency, safety, and quality. As technology continues to advance, new features in automation will open up even more possibilities for innovation and growth.
Industrial automation encompasses a range of essential functions that streamline and optimize manufacturing processes. Here are some key functions of industrial automation:
1. Process Control
Purpose: To regulate the parameters of various manufacturing processes, such as temperature, pressure, flow rate, and speed.
How it Works: Sensors and control systems like PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) and DCS (Distributed Control Systems) monitor these parameters, adjusting them in real-time to ensure optimal operation. This maintains consistent quality and performance across production lines.
2. Quality Assurance and Inspection
Purpose: To maintain high quality standards by detecting defects or deviations in products.
How it Works: Automation uses sensors, cameras, and AI-driven image recognition software to inspect products on the line, identifying any quality issues such as defects or misalignments. This minimizes human error and reduces the likelihood of defective products reaching customers.
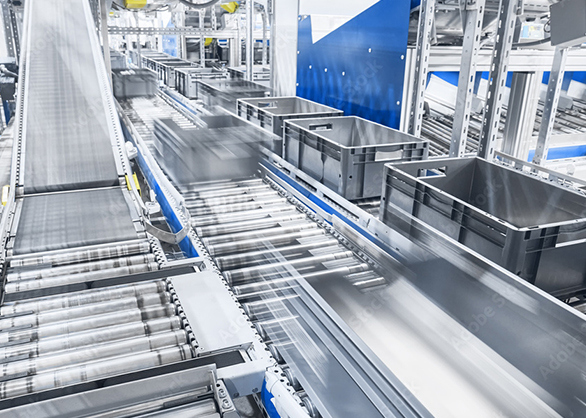
3. Material Handling
Purpose: To move, store, and organize materials throughout the production process.
How it Works: Automated material handling systems like conveyor belts, robotic arms, and AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles) transport raw materials and finished products between different stages of production, storage, and shipping. This improves efficiency and reduces manual labor.
4. Assembly and Packaging
Purpose: To assemble components and package products with high speed and accuracy.
How it Works: Robots and automated assembly lines handle precise tasks such as welding, screwing, labeling, and packaging. By performing these tasks with consistent accuracy, automation ensures uniform quality and enhances production speed.
5. Data Collection and Analysis
Purpose: To gather data on every aspect of production for analysis and decision-making.
How it Works: Industrial automation systems collect data from sensors, machinery, and production software. This data is analyzed to optimize processes, reduce waste, and improve efficiency. It also aids in predictive maintenance, product development, and quality improvements.
6. Inventory and Supply Chain Management
Purpose: To optimize inventory levels and streamline supply chain operations.
How it Works: Automated systems track inventory in real-time, monitor stock levels, and communicate with suppliers. This minimizes excess inventory and ensures that materials and components are always available, reducing production downtime.
7. Predictive Maintenance
Purpose: To identify potential equipment failures before they occur, minimizing downtime.
How it Works: Sensors monitor machine health metrics, such as temperature, vibration, and usage patterns. AI-driven predictive maintenance systems analyze this data, signaling when maintenance is needed to prevent breakdowns.
8. Energy Management
Purpose: To reduce energy consumption and improve sustainability.
How it Works: Automation systems regulate energy usage in machinery, lighting, and climate control based on real-time needs. By optimizing power usage, these systems lower energy costs and reduce environmental impact.
9. Product Customization and Flexibility
Purpose: To enable the production of customized products without significant reconfiguration.
How it Works: With automation, manufacturers can quickly adapt to product design changes and run different product configurations on the same line, enabling a higher degree of flexibility in production.
10. Logistics and Warehouse Management
Purpose: To optimize storage, retrieval, and shipping of products.
How it Works: Automated storage and retrieval systems (ASRS), conveyor belts, and robotic forklifts streamline warehouse operations. This reduces human involvement, speeds up processing, and ensures efficient use of storage space.
11. Safety and Hazard Control
Purpose: To minimize risk in hazardous working environments.
How it Works: Robots and automated systems perform dangerous tasks, such as handling toxic materials or working in extreme conditions, ensuring worker safety and compliance with safety regulations.
12. Batch and Continuous Production Control
Purpose: To manage production cycles and ensure a smooth flow of operations.
How it Works: Automated control systems allow seamless transitions between batch and continuous production processes, adjusting for demand and product specifications. This function is especially useful in industries like pharmaceuticals, food, and chemicals.
By integrating these functions, industrial automation allows manufacturers to enhance productivity, minimize costs, ensure quality, and respond flexibly to market demands. These capabilities have transformed traditional production environments, making them smarter, safer, and more sustainable.
Industrial automation is crucial to modern manufacturing and has significant implications across various industries. Here’s why it’s important:
1. Increases Productivity
Automated systems can work 24/7 without the need for breaks, increasing production output. This continuous operation boosts productivity, enabling manufacturers to meet high demand and improve overall efficiency.
2. Enhances Product Quality
Automation allows for precise control over production parameters, which results in higher quality and consistent products. Automated systems minimize human error, detect defects early, and ensure that each product meets set standards, improving customer satisfaction and reducing product recalls.
3. Reduces Operational Costs
While the initial investment in automation technology can be high, it reduces long-term operational costs by decreasing labor costs, minimizing waste, and reducing the likelihood of costly errors. Predictive maintenance also lowers expenses related to equipment downtime and repairs.
4. Improves Workplace Safety
Industrial automation helps remove workers from hazardous environments, where they may be exposed to high temperatures, toxic chemicals, or heavy machinery. By using robots and other automated systems, industries can reduce workplace injuries, comply with safety regulations, and create a safer environment.
5. Enables Flexibility and Adaptability
Automated systems can be reprogrammed to accommodate product design changes, offering greater flexibility for production. This allows manufacturers to switch between different products on the same line, helping them respond quickly to changing market demands and customer preferences.
6. Provides Real-Time Data and Insights
Industrial automation systems collect data from various production stages, enabling real-time monitoring, quality control, and analytics. This data-driven approach supports informed decision-making, process optimization, and continuous improvement.
7. Supports Environmental Sustainability
Automation systems are designed to optimize resource use, leading to less waste and energy consumption. This promotes sustainable practices by reducing the environmental impact of production, helping companies meet green standards and regulatory requirements.
8. Facilitates Innovation
With automation handling routine tasks, employees are freed up for more innovative, creative, and strategic roles. This shift allows companies to focus on product development, new technologies, and improved processes that drive long-term growth.
9. Improves Supply Chain and Inventory Management
Automated inventory systems keep track of stock levels and supply needs in real-time, ensuring that materials are always available. This reduces stockouts, minimizes excess inventory, and helps maintain a smooth production flow.
10. Enhances Competitiveness
Companies that adopt automation can operate more efficiently, produce high-quality products at lower costs, and respond quickly to market demands. This boosts their competitiveness in a global market, allowing them to expand and reach new customers.
11. Supports Global Standardization
Industrial automation helps manufacturers adhere to global quality and safety standards. Consistency in production quality is essential for companies looking to expand internationally, as they must meet regulatory requirements across different regions.
Industrial automation is foundational to the future of manufacturing, enhancing productivity, sustainability, and innovation. It is vital for any industry looking to maintain competitive advantages, reduce costs, and achieve growth in an increasingly complex and connected world.
The relevance of industrial automation is profound and far-reaching, particularly in today’s fast-paced, highly competitive global market. Here’s why it remains critical:
1. Economic Growth and Competitiveness
Industrial automation plays a pivotal role in boosting economic growth by enabling faster, more efficient production, which lowers the cost of goods. Companies can produce high-quality products at lower costs, enabling them to compete in both local and international markets. This competitiveness fosters innovation and supports economic expansion.
2. Labor Market Transformation
As automation takes over repetitive or hazardous tasks, the labor market shifts toward more specialized, skilled roles. This transformation not only enhances job satisfaction but also opens new employment opportunities in fields like robotics, data analysis, and systems management. Automation's relevance lies in its ability to elevate human roles, driving workforce development in technical and innovative areas.
3. Environmental Sustainability
Automation technologies help industries reduce their carbon footprint by optimizing energy consumption and minimizing waste. For companies aiming to meet environmental standards and regulatory requirements, automation is an essential tool for building more sustainable practices. It also plays a significant role in resource-intensive industries, such as manufacturing and energy, where efficiency is directly linked to reduced environmental impact.
4. Enhanced Quality and Reliability
With automation, industries can ensure consistent product quality, reliability, and adherence to standards. This relevance is especially critical in sectors like healthcare, automotive, and electronics, where quality control can impact consumer safety. Automated processes maintain a high level of precision, ensuring that products meet stringent quality requirements, which fosters consumer trust and brand loyalty.
5. Support for Supply Chain Efficiency
Automated systems streamline supply chain operations by accurately managing inventory, tracking materials, and optimizing logistics. This is essential for preventing stock shortages, reducing excess inventory, and ensuring on-time delivery. In a globalized economy where supply chain disruptions can cause significant losses, automation keeps supply lines efficient and resilient.
6. Response to Market Demands and Customization
Industrial automation allows companies to adapt quickly to changing market demands, customer preferences, and product innovations. Automated processes are flexible and can be reprogrammed to handle product variations and customization, making it easier for businesses to stay relevant and responsive in dynamic markets.
7. Increased Safety Standards
Automation has greatly reduced the need for human workers to perform dangerous tasks, enhancing workplace safety and lowering the rate of accidents and injuries. For industries dealing with hazardous materials or environments, automation’s role is crucial in creating a safer, healthier workplace and complying with safety regulations.
8. Foundation for Smart Manufacturing and IoT
Industrial automation serves as the backbone for smart factories and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). By connecting machines, systems, and devices, automation enables seamless data exchange and real-time monitoring, making production smarter, faster, and more connected. As digital transformation progresses, automation’s relevance will only grow, serving as the foundation for advanced manufacturing technologies.
9. Adaptability for Industry 4.0
As industries move toward Industry 4.0, with interconnected devices, AI, and machine learning, automation becomes even more relevant. It prepares businesses for the future by integrating smart technology into production, which enhances operational insights and supports predictive maintenance, quality assurance, and resource planning.
10. Scalability for Business Growth
Automation allows businesses to scale operations up or down without significant delays or additional costs, supporting both rapid expansion and efficient downsizing. This flexibility enables companies to grow sustainably and manage production in response to market conditions.
11. Customer Satisfaction and Service
Automated systems ensure timely production and consistent product quality, which directly contributes to customer satisfaction. For businesses, the ability to deliver quality products quickly and reliably is key to building lasting relationships with customers, which is fundamental in today’s customer-centric economy.
Industrial automation remains relevant across a variety of sectors because it addresses the demands of quality, efficiency, flexibility, and sustainability that define modern manufacturing. It enables companies to thrive in a globalized economy, supports the shift to greener practices, and lays the foundation for innovation in the coming digital age.